Understanding Automation: [AGVs, AMRs, and AIVs]
Different Types of Automation

Why Automate Your Manufacturing Process?
The use of automation technology has become increasingly popular due to its ability to increase production speed and deliver consistent results. Automation can be utilized in the manufacturing industry for tasks ranging from small warehouse operations to moving objects weighing over 100,000 pounds in a production line. With its significant return on investment, automation has become an important element in the manufacturing industry.

Understanding the Differences: AGVs vs. AMRs vs. AIVs
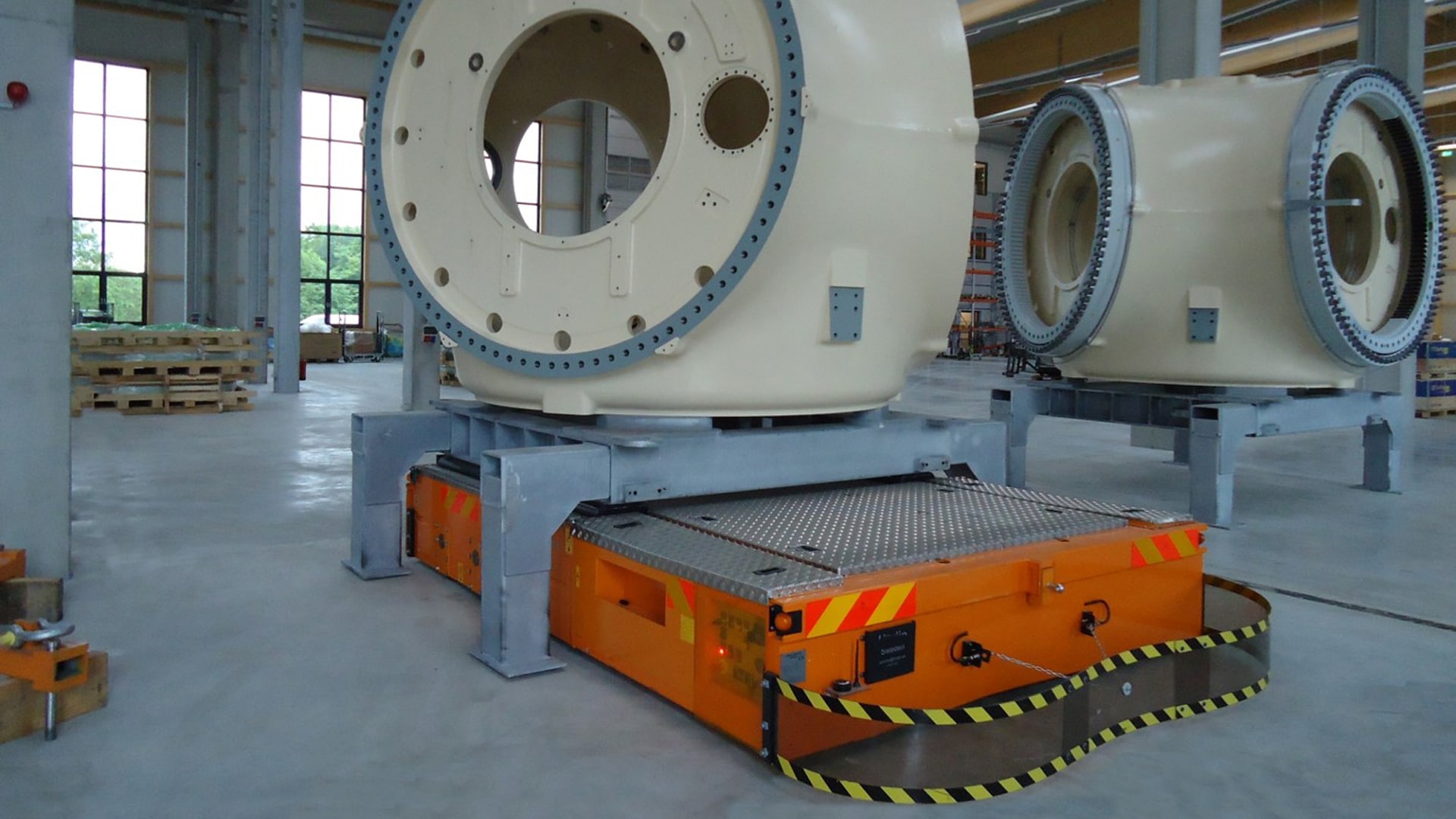
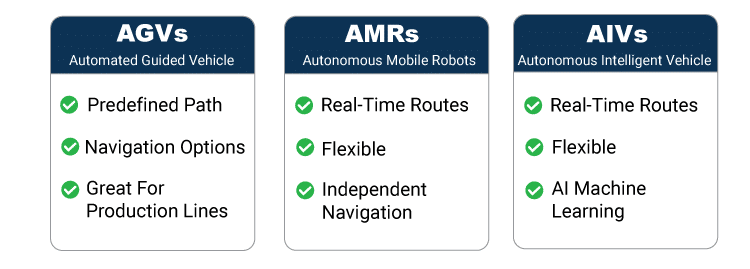
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), and Autonomous Intelligent Vehicles (AIVs) represent different approaches for automation in material handling. Each of these systems has unique characteristics, advantages, and applications. This article will explain the differences between these technologies.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
Robotic systems that transport materials along predefined paths
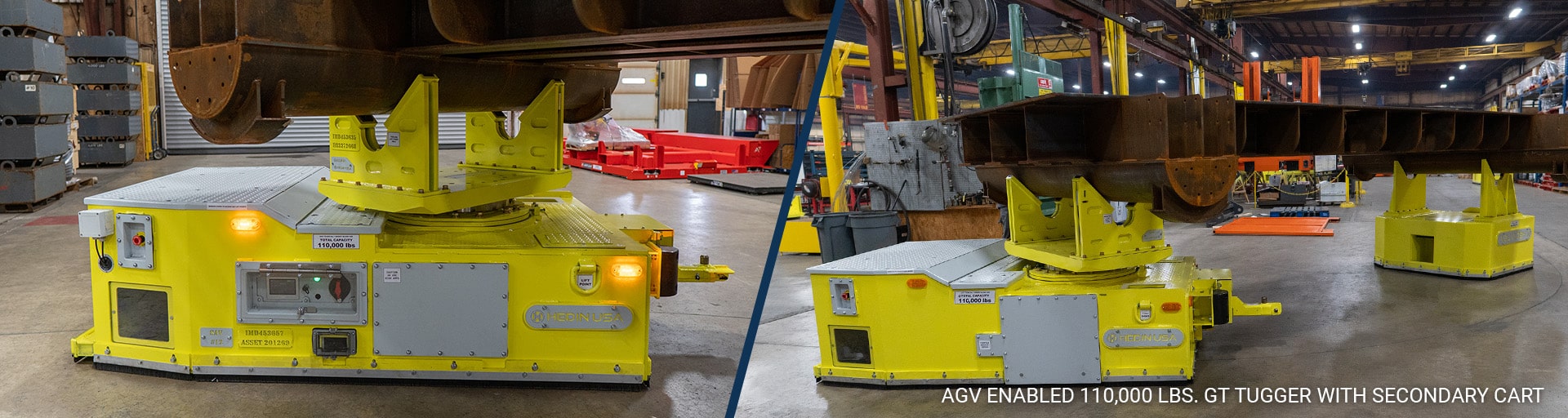
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), also known as Self-Guided Vehicles (SVGs), are robotic systems designed to transport materials within a facility along predefined paths without a human operator. They are equipped with their own drive units and navigate using various guidance systems, such as magnetic strips, wires, or sensors. AGVs are used in environments with consistent and predictable material flows, such as a production line.
Navigation and Safety
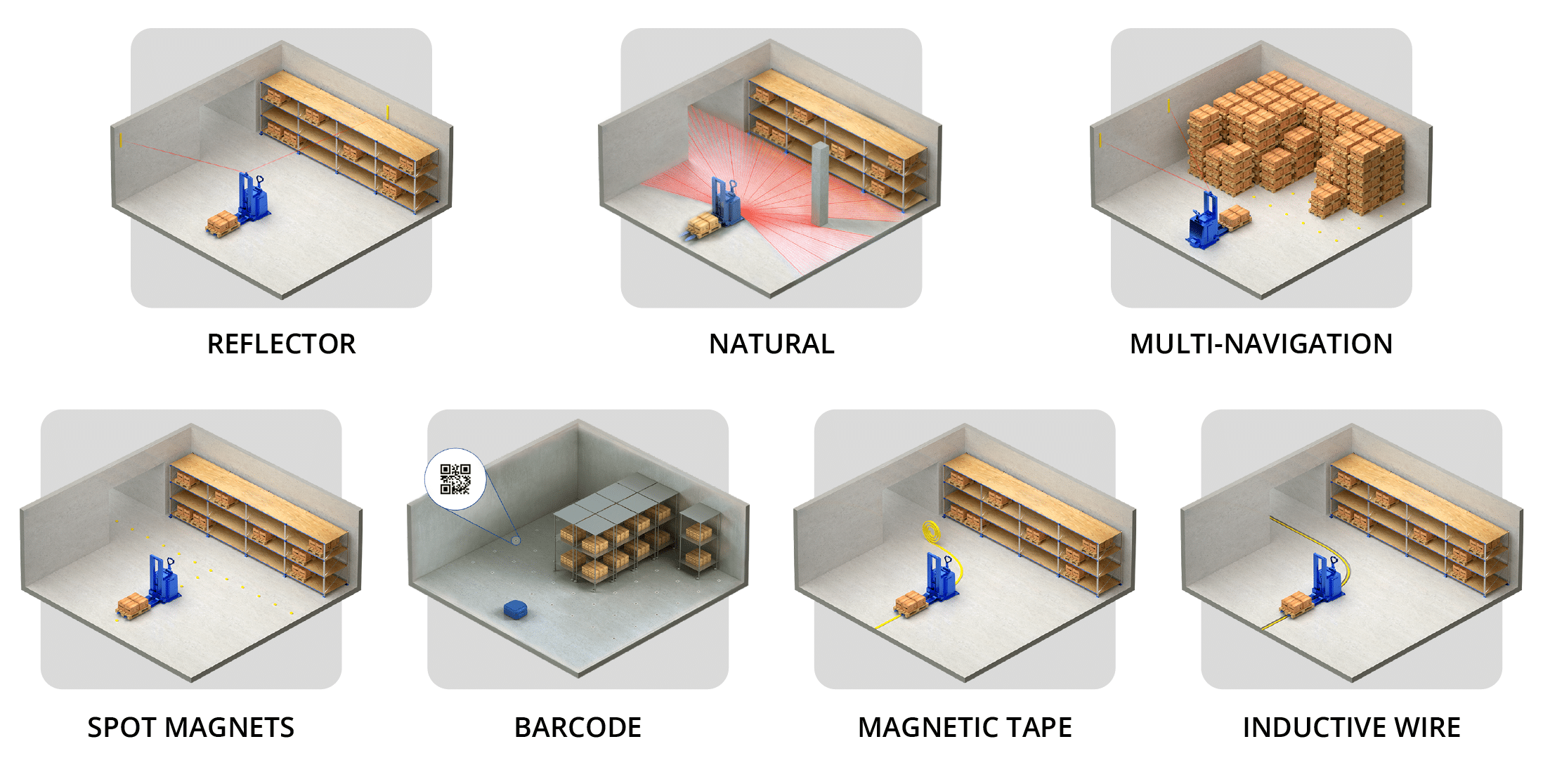
AGVs typically follow fixed, predefined routes and can require infrastructure modifications, such as the installation of magnetic tapes or inductive wires. Align Production Systems offers several navigation options for AGVs, including:
- Laser Positioning using Reflectors (LiDAR)
- Machine Learning with Natural Navigation
- Series of Physical Markers like Magnetic Spots and Barcodes
- Line Following with Magnetic Tape and Inductive Wire
- Combination of Systems for Multi-Navigation
Safety is always important in AGV systems. Align Production Systems ensures that their AGVs are equipped with multiple safety features, including:
- Safety Scanners for Collision Avoidance
- Visual and Audible Warnings
- Emergency Stop Buttons
- Creep Zones to Slow Down in Certain Areas
Applications
AGVs follow a programmed path and are best used for repetitive tasks in environments with minimal changes or obstacles. They are commonly used in warehouses, manufacturing plants, and distribution centers. Align Production Systems provides AGVs for heavy industry with high-capacity capabilities, automating movement for the heaviest of loads.
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
Advanced robotic systems that navigate independently using AI and sensors
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are advanced robotic systems that navigate independently using digital maps, sensors, and artificial intelligence. Unlike AGVs, AMRs do not require path programming and can plan their routes in real time.
Navigation and Flexibility
AMRs use navigation technologies such as cameras, laser scanners, and AI to detect and avoid obstacles. This allows them to operate in dynamic environments where paths and tasks frequently change. AMRs are highly flexible and can adapt to various tasks with minimal infrastructure changes.
Applications and Advantages
AMRs are ideal for environments that require high flexibility and adaptability, such as warehouses. They are used in applications such as picking, inventory management, and sortation.
Autonomous Intelligent Vehicles (AIVs)
Next-generation robotic systems with continuous learning and adaptation capabilities
Autonomous Intelligent Vehicles (AIVs) are the next generation of robotic systems. They combine the best features of AGVs and AMRs and operate without human intervention. AIVs are equipped with advanced AI algorithms, allowing them to continuously learn and adapt to their environment. They can plan their own route to their destination with minimal obstacles, unlike AGVs which require predefined routes.
Navigation and Intelligence
AIVs use a combination of AI, machine learning, and sensors to navigate obstacles and people in their path. They can perform tasks such as route selection, obstacle avoidance, and route optimization in real time.
Applications and Future Prospects
AIVs are designed to operate in highly dynamic and unpredictable environments. They are utilized in advanced manufacturing, research facilities, and smart warehouses. The continuous learning capability of AIVs makes them a promising solution for future automation needs, as they can learn the best path on their own.

Conclusion
Choosing the right automation system depends on your manufacturing needs and the operating environment. AGVs, provided by Align Production Systems, are ideal for environments with high capacity, consistent material flows, and predefined paths. AMRs offer greater flexibility and are suited for dynamic environments, while AIVs represent the cutting edge of autonomous robotics with continuous learning and adjusting to change. By understanding the differences between these technologies, you can make informed decisions to optimize your material handling processes and improve overall productivity.